Electromagnetic Spectrum – What are Gamma Waves?
Electromagnetic spectrum definition
Electromagnetic spectrum, the entire distribution of electromagnetic radiation according to frequency or wavelength. Although all electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, they do so at a wide range of frequencies, wavelengths, and photon energies.
The electromagnetic spectrum comprises the span of all electromagnetic radiation and consists of many sub ranges, commonly referred to as portions, such as visible light or ultraviolet radiation. The various portions bear different names based on differences in behavior in the emission, transmission, and absorption of the corresponding waves and also based on their different practical applications.
There are no precise accepted boundaries between any of these contiguous portions, so the ranges tend to overlap.
Electromagnetic spectrum diagram
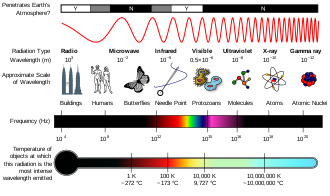
Diagram
Electromagnetic spectrum examples
Radio waves have the longest wavelength and smallest frequency. They can travel long distances, but are not high energy waves, so they cannot penetrate through solid substances very well. This is why you might not be able to pick up a radio signal when you are driving between two mountains or when you are underground.
Microwaves have frequencies that are higher than radio waves but lower than infrared waves. Microwaves are used for more than just cooking food, although they are great at that because they can make water molecules vibrate, heating them up very quickly. Microwaves are also used by cell phones, in radar guns that the police use to detect how fast you are driving, and also used by weather forecasters to predict the motion of clouds and storms.
The electromagnetic spectrum includes everything from radio waves to light waves to gamma rays
With frequencies just below those of visible light, infrared waves transmit heat. When you sit outside on a sunny day, it’s mainly the infrared waves from the sun that make you feel warm. Infrared cameras can detect infrared waves, so they can see people and animals even in the dark because we are always giving off heat!
Visible light is right in the middle of the spectrum, and it makes up only a very small segment of the entire electromagnetic spectrum. The wavelengths of visible light range from about 700 nm for red light to 400 nm for violet light.
What are gamma waves?
A gamma wave is a pattern of neural oscillation in humans with a frequency between 25 and 100 Hz, though 40 Hz is typical.
According to a popular theory, gamma waves may be implicated in creating the unity of conscious perception (the binding problem).However, there is no agreement on the theory.
Whether or not gamma wave activity is related to subjective awareness is a very difficult question which cannot be answered with certainty at the present time. (As found on Wikipedia)
What are gamma brain waves?
Gamma brain waves are a frequency pattern of normal brain activity that measures between 25 and 100 Hz, with around 40 Hz being typical in humans.
Gamma waves were essentially unknown before the development of digital EEG.
Neuro scientist are now beginning to discover the marvelous properties of the brain when it produces the gamma frequency.
| Additional reading: | |
| Title: | HTML: |
| Types of electromagnetic waves | |
| What are Gamma Brain Waves? | |
| What are gamma waves | Benefits of gamma waves | |
| Gamma Brain Waves | |
Tags: Electromagnetic Spectrum, Gamma Waves

